SOC 2 Compliance – SOC 2 Penetration Testing – In an environment where data holds significant value, safeguarding it from unauthorized access is crucial. Government compliance standards related to cyber data establish security policies and regulations, offering guidance to ensure organizations implement proper security measures. This is essential to protect sensitive user data and prevent unauthorized access by hackers.
A robust offense is deemed the most effective defense. This philosophy underlies the cybersecurity approach of “ethical hacking,” commonly referred to as penetration testing (pen-testing). To comprehensively identify vulnerabilities that cybercriminals might exploit and understand their potential methods, it is advisable to conduct testing internally or seek assistance from a proficient service provider. Pen-testing proves particularly beneficial for verifying the implementation of regulatory standards, including those essential for SOC 2 compliance. So, learn and understanding SOC 2 compliance is paramount for organizations entrusted with customer data.
Achieving SOC 2 compliance necessitates organizations to establish thorough policies and procedures for managing cybersecurity risks. Furthermore, they are required to undergo periodic independent audits to verify the adequacy of their systems’ security measures.
What Does SOC 2 Compliance Entail?
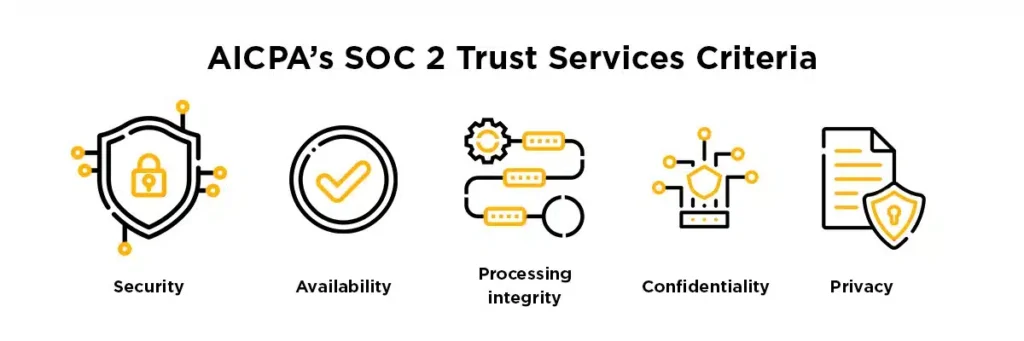
SOC 2, crafted by the American Institute of CPAs, establishes criteria for overseeing customer data, focusing on five “trust service principles”: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. It’s crucial to understand that SOC 2 is not a certification but rather an auditor’s opinion.
SOC 2, which stands for Service and Organization Controls 2, comprises a set of standards that organizations must follow to guarantee the implementation of policies and practices aimed at fortifying the security of their systems and data. The oversight of this framework lies with the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA).
Achieving SOC 2 compliance necessitates organizations to establish thorough policies and procedures for managing cybersecurity risks. Furthermore, they are required to undergo periodic independent audits to verify the adequacy of their systems’ security measures.
What are SOC 2 penetration testing and vulnerability scanning?
Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning emerge as crucial components for evaluating computer system security and validating an organization’s overall security stance, assessing controls crafted to ward off cyber attacks.
Termed as “pentest,” penetration testing entails a simulated attack utilizing the same tools, tactics, techniques, and procedures as adversaries. This ethical security testing aims to uncover vulnerabilities, exploit weaknesses, and illustrate the potential impact on a specific system, network, or the entire organization.
The demonstrated impact may manifest in various forms, such as accessing confidential assets like customer data or sensitive information at the strategic, board-level.
Conversely, vulnerability scanning is an automated process striving to identify known vulnerabilities, providing insights into the company’s security posture.
While both penetration testing and vulnerability scanning contribute to identifying security risks, they possess distinct strengths and weaknesses. Penetration testing is more likely to unveil unknown vulnerabilities but is resource-intensive and costly. In contrast, vulnerability scanning, though swifter and more economical, is less likely to detect vulnerabilities deviating from established patterns.
What are the differences between SOC 2 Type I and Type II?
There exist two types of AICPA SOC 2 attestation reports—SOC 2 Type I and Type II. Here’s a breakdown of their distinctions:
- SOC 2 Type I:
This report delves into an organization’s information security controls at a specific point in time. The objective is to evaluate the suitability and existence of these controls, ensuring they align with their intended purpose. - SOC 2 Type II:
In contrast, this report assesses an organization’s security controls over a designated period, typically spanning 3-12 months. The primary aim is to ascertain whether these controls operate as intended and meet the criteria outlined in AICPA’s Trust Services Criteria. Type II reports are more extensive, offering valuable insights for customers evaluating an organization’s sustained commitment and strategic approach to cybersecurity.
What Controls Does SOC 2 Require, and For Which Companies?
As previously mentioned, SOC is anchored in the AICPA’s Trust Services Criteria (TSC), a relatively straightforward framework encompassing five fundamental “trust categories” or principles:
- Security: Guarding against unauthorized access, information disclosure, and misuse.
- Availability: Providing data access to users with the right or privilege to access it.
- Processing Integrity: Ensuring that all processes operate according to their design.
- Confidentiality: Safeguarding unique and sensitive information within defined limits.
- Privacy: Restricting the collection, use, and retention of personal information.
These principles further break down into nine common criteria (CC) series within the security category and four additional criteria series for the remaining categories. Within each series, numerous individual controls and sub-controls exist, accompanied by explanatory “points of focus.” It is within these points of focus that penetration testing finds mention.
Is penetration testing a requirement for SOC 2?
The response is no. While penetration testing holds value for organizations, it is not obligatory for achieving or maintaining SOC 2 compliance. Nevertheless, auditors frequently propose penetration testing assessments to enhance the audit process and fulfill specific criteria outlined in Trust Services Criteria (Monitoring activities):
- According to COSO Principle 16: “The entity selects, develops, and performs ongoing and/or separate evaluations to ascertain whether the components of internal control are present and functioning.”
- Furthermore, CC4.1’s point of focus states: “Management uses a variety of different types of ongoing and separate evaluations, including penetration testing, independent certifications made against established specifications (for example, ISO certifications), and internal audit assessments.”
How does penetration testing fit into the SOC 2 criteria, and what alternative methods might fulfill the requirements?
The SOC 2 criteria alludes to the inclusion of penetration testing as one of the approaches for conducting necessary evaluations. However, an auditor might assert that your organization’s existing ISO 27001 certificate adequately meets the stipulated requirements.
Drawing from our experiences, there have been instances where an auditor accepted a customer’s public bug bounty program as evidence to fulfill CC4.1. Interpretation plays a significant role, yet there is undeniable importance in acknowledging penetration testing as a vital step in meeting this requirement. Beyond compliance, it offers the substantial advantage of uncovering potential risks and fortifying your organization’s resilience against cyber attacks.
What are the Requirements for SOC 2 Penetration Testing?
The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) devised Service and Organization Controls (SOC) based on its Trust Services Criteria (TSC) to safeguard companies storing sensitive financial data. Penetration testing is a crucial element for many companies seeking to adhere to these criteria and achieve successful SOC 2 reporting. The question arises: Is it a mandatory requirement?
This discussion aims to explore two perspectives in addressing whether your company must incorporate penetration testing for SOC 2 compliance and bolstering cybersecurity:
- The concise response: Technically, there are no explicit requirements for penetration testing in SOC 2.
- The comprehensive response: Nevertheless, it is highly advisable to integrate penetration testing for SOC 2, and here’s why.
Examining both viewpoints provides a comprehensive understanding of the SOC 2 penetration testing requirements.
Concise Response: No Strict SOC 2 Penetration Testing Requirements
In the realm of optimizing cyber defenses, penetration testing stands out as a potent and versatile analytical tool. However, it’s noteworthy that SOC 2 compliance doesn’t strictly mandate penetration testing. The most recent update to the Trust Services Criteria (TSC) in 2020 features “penetration testing” just once, not as a control but as one of the various “different types of ongoing and special evaluations” organizations may consider as an additional focus.
Despite its non-mandatory status, dismissing the potential of penetration testing would be a oversight.
SOC 2 compliance exhibits a certain leniency compared to stringent requirements seen in other regulatory compliance frameworks. Rather than imposing a set of controls, SOC 2 provides principles for companies to contemplate while devising their adaptable solutions.
But, Does SOC 2 Actually Require Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing is not obligatory for obtaining SOC 2 compliance. However, it is imperative to establish controls ensuring the detection and prevention of unauthorized access to systems, applications, and data.
The journey towards SOC 2 compliance is intricate, often presenting a daunting challenge for many companies. The audit scope is extensive, and the process demands careful attention to avoid pitfalls.
A notable challenge in SOC 2 compliance lies in the ambiguity surrounding the necessity of specific practices. Although penetration testing is not mandated for SOC 2, its execution serves as an invaluable tool to pinpoint vulnerabilities and uncover weaknesses in security. Moreover, it aids companies in prioritizing cybersecurity efforts effectively.
Beyond its role in achieving SOC 2 compliance, penetration testing emerges as a crucial component of an overarching security strategy, forming an integral part of a company’s risk management approach.
Another SOC 2 Penetration Testing requirements
Penetration testing, while not obligatory, is explicitly highlighted in the SOC 2 Type II Points of Focus.
As per CC4.1 (Additional points to focus):
“Management utilizes various ongoing and distinct evaluations, including penetration testing, independent certifications against established specifications (such as ISO certifications), and internal audit assessments.”
From this, it is evident that conducting SOC 2 penetration testing is not mandatory. However, it plays a crucial role in identifying and effectively managing security risks.
Why is SOC 2 penetration testing still recommended, despite not being a mandatory requirement?
Comprehensive Response: The Continued Relevance of SOC 2 Penetration Testing
Even though penetration testing is not obligatory for SOC 2 compliance, it remains a formidable tool with the capacity to fulfill other audit requirements and safeguard stakeholders. As previously highlighted, the AICPA’s TSC acknowledges penetration testing as a viable option for robust vulnerability and risk monitoring (refer to CC4.1). Let’s delve into two aspects:
- The specific practice of penetration testing in internal, external, and hybrid forms
- The broader domain of vulnerability management, encompassing vulnerability scans
Both practices stand as indispensable components of a robust cyber defense architecture, paralleling fundamental measures like firewalls and antivirus software. Given the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats, embracing advanced criteria becomes imperative to effectively address and counteract these challenges.
Is vulnerability scanning a requirement for SOC 2 compliance?
SOC 2 compliance doesn’t mandate vulnerability scanning. However, it stands as a recommended best practice integral to any robust cybersecurity initiative.
While not obligatory, vulnerability scanning contributes to fulfilling specific requirements outlined in the Trusted Services Criteria, particularly in System Operations:
- CC7.1: “To meet its objectives, the entity uses detection and monitoring procedures to identify (1) changes to configurations that result in the introduction of new vulnerabilities, and (2) susceptibilities to newly discovered vulnerabilities”
- CC7.1 point of focus: “Conducts Vulnerability Scans — The entity conducts vulnerability scans designed to identify potential vulnerabilities or misconfigurations on a periodic basis and after any significant change in the environment and takes action to remediate identified deficiencies on a timely basis.”

It’s crucial to note that vulnerability scanning, while a supportive activity aligning with CC7.1, is not obligatory. Nevertheless, companies are encouraged to integrate regular vulnerability scans into their security protocols. This proactive measure gains significance considering that 60% of data breaches are attributed to vulnerabilities stemming from inadequate system updates and delayed patching, as reported by.
Should my organization include penetration testing and vulnerability scanning in the SOC 2 compliance audit?
Indeed, penetration testing and vulnerability assessments are not obligatory components for achieving SOC 2 compliance. However, considering the evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats impacting businesses globally, they can play a pivotal role in fortifying your organization’s resilience and enhancing defenses against ransomware, data breaches, and emerging threats.
The combination of vulnerability scanning and penetration testing serves as a valuable toolset for assessing the efficacy of your security controls and pinpointing areas in need of IT security enhancements. Together, these practices form an integral aspect of a comprehensive security program. Regularly conducting such activities ensures ongoing protection for your systems against diverse cyber threats.
How Can Penetration Testing Help In SOC 2 Compliance?
In recent times, an increasing number of organizations are undergoing compliance audits to showcase their adherence to various industry laws, regulations, and standards. Within these audits, vulnerability scans and penetration tests play a crucial role.
- Penetration Testing stands as a integral aspect of SOC 2 compliance, garnering significant attention from the compliance committee. This pivotal check is part of a comprehensive testing process primarily conducted by security engineers and teams.
- Both Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Scanning are essential components of SOC 2 compliance, a set of codes and standards meticulously designed to align a company’s Security and IT Controls with the security and privacy expectations of its customers.
- In today’s digital landscape, where privacy breaches are not uncommon, SOC 2 compliance holds paramount importance. The SOC 2 Compliance report serves as tangible proof to customers that their data remains secure. Moreover, these reports offer a platform to elucidate the steps taken to safeguard customer data.
- Penetration Testing and Vulnerability Scanning, distinct yet interconnected checks, constitute integral elements of the SOC 2 compliance process. Their execution ensures that the security of data aligns seamlessly with the promises made to customers.
Some benefits of regular pentests include:
- Assisting organizations in comprehending and enhancing their security posture.
- Ensuring the protection of data from cyber-criminals.
- Cost savings by preventing potential data breaches.
- Mitigating the risk of hackers exploiting security vulnerabilities.
How can penetration testing be optimized for SOC 2 compliance?
Penetration testing stands out as a sophisticated approach in cyber defense, providing unparalleled insights into potential vulnerabilities. It employs real-time analytics to simulate how a hacker might compromise a system. For SOC 2 purposes, two primary forms of pen-testing prove valuable:
- External Testing:
Also known as “black hat” or “black box” testing. The attacker commences without prior knowledge of your systems. The objective is to comprehend the entire process, identifying points of attack and entry. Particularly effective for assessing processing integrity and security. - Internal Testing:
Also known as “white hat” or “white box” testing. The attacker starts with privileged knowledge about your company. Focuses on understanding the hacker’s movements once inside, providing insights into monitoring availability during and after an attack. Many companies adopt a hybrid approach, often termed “grey hat” or “grey box” testing, representing an excellent strategy to tailor pen-testing to SOC 2 requirements. Depending on the existing security structures for confidentiality, privacy, or availability, a pen-test that begins externally and transitions internally can effectively assess all three categories simultaneously.
Unraveling the Timelines and Costs of SOC 2 Penetration Tests
The average duration of a SOC 2 pentest
Understanding the typical duration of a SOC 2 penetration test is crucial for organizations seeking to fortify their cybersecurity. The timeframe generally spans from 5 to 25 person days, contingent upon the project’s scope. While assessing the cybersecurity of a single website or web application may necessitate only a few days, more extensive endeavors such as evaluating large cloud infrastructures or intricate SaaS platforms might extend over several weeks. Notably, penetration tests for SaaS companies typically conclude within one to two weeks, although larger scopes may demand additional time.
It’s important to exercise caution when confronted with providers offering “express” penetration tests lasting one to three days. Such abbreviated assessments may rely heavily on automated scanners or basic checklists, potentially overlooking subtle vulnerabilities, particularly those rooted in an application’s business logic. Experience has shown that a SOC 2 penetration test lasting less than 40 hours for a small to medium-sized scope may lack the requisite level of scrutiny.
The estimated cost of a SOC 2 penetration test
Determining the financial investment for a SOC 2 penetration test conducted by a reputable and accredited cybersecurity firm is a vital consideration for organizations. The average estimated cost typically falls within the range of $7,000 to $25,000, contingent upon the project’s scope and complexity. While more extensive security audits may incur higher costs, smaller scopes might yield more economical estimates. Reputable penetration test providers commonly charge around $250 to $300 per hour for their services.
It’s crucial to approach providers offering significantly lower prices with caution. Such offerings may heavily rely on automated scanners or enlist inadequately qualified pentesters, potentially resulting in superficial evaluations that, while appeasing auditors, leave systems vulnerable and create a false sense of security.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, comprehending and adhering to SOC 2 compliance is essential for organizations entrusted with safeguarding customer data. SOC 2, established by the American Institute of CPAs, sets stringent criteria, focusing on five trust service principles: security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy. Achieving SOC 2 compliance requires meticulous policies, periodic audits, and adherence to the AICPA’s Trust Services Criteria. Penetration testing and vulnerability scanning, though not mandatory, play vital roles in assessing cybersecurity. The distinctions between SOC 2 Type I and Type II reports highlight the significance of evaluating security controls over time. While penetration testing is not obligatory, its continued relevance is emphasized, offering valuable insights into potential risks and enhancing overall cybersecurity.
Organizations are encouraged to integrate these practices into their security protocols, considering the evolving landscape of cyber threats. The timelines and costs associated with SOC 2 penetration tests underscore the importance of thorough assessments, cautioning against abbreviated evaluations that may compromise the scrutiny required for effective security measures. Ultimately, the investment in SOC 2 compliance, both in terms of time and cost, is a proactive approach to fortify organizational resilience and protect against diverse cyber threats in the ever-evolving digital landscape.



